“A good programmer is someone who always looks both ways before crossing a one-way street.”
The Fibonacci numbers, commonly denoted F(n) form a sequence, called the Fibonacci sequence, such that each number is the sum of the two preceding ones, starting from 0 and 1. That is,
F(0) = 0, F(1) = 1
F(n) = F(n - 1) + F(n - 2), for n > 1.
Given n, calculate F(n).
Example 1:
Input: n = 2
Output: 1
Explanation: F(2) = F(1) + F(0) = 1 + 0 = 1.
相信大家都用遞迴寫過費氏數列的題目:
class Solution(object):
def fib(self, n):
"""
:type n: int
:rtype: int
"""
if n <= 1:
return n
return self.fib(n - 1) + self.fib(n - 2)
記憶化遞迴:
class Solution(object):
def fib(self, n, memo={}):
"""
:type n: int
:rtype: int
"""
if n in memo:
return memo[n]
if (n <= 1):
return n
memo[n] = self.fib(n - 1, memo) + self.fib(n - 2, memo)
return memo[n]
比較一下普通遞迴跟記憶化遞迴的速度差異: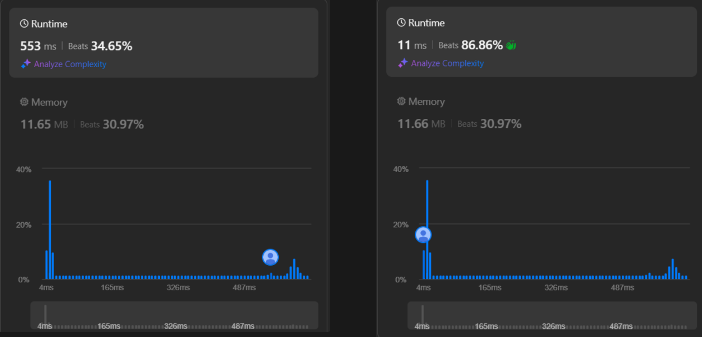
因為普通遞迴重複計算了已經算過的值,舉例來說fib(5) = fib(4) + fib(3),再繼續往下拆解,
fib(4) = fib(3) + fib(2),有發現了嗎?又算了一次fib(3),因為遞迴內的子函數不知道外面有已經算好的值。
記憶遞迴透過把算過的值記錄下來,一旦發現已經算過了,那就直接拿算過的值回傳!
剛剛的遞迴是由頂向下的(fib(5)一層一層拆到fib(1)和fib(0)),而且需要我們手動去做記憶。
而動態規劃是由底向上的,而且自帶記憶!
class Solution(object):
def fib(self, n, memo={}):
"""
:type n: int
:rtype: int
"""
if n <= 1: # 如果n是0或1,會導致下面迴圈越界!
return n
dp = [0] * (n + 1)
dp[0] = 0 # 初始條件
dp[1] = 1 # 初始條件
for i in range(2, n + 1):
dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2]
return dp[n]
You are climbing a staircase. It takes n steps to reach the top.
Each time you can either climb 1 or 2 steps. In how many distinct ways can you climb to the top?
Example 1:
Input: n = 2
Output: 2
Explanation: There are two ways to climb to the top.
1. 1 step + 1 step
2. 2 steps
Example 2:
Input: n = 3
Output: 3
Explanation: There are three ways to climb to the top.
1. 1 step + 1 step + 1 step
2. 1 step + 2 steps
3. 2 steps + 1 step
題目問說一次爬1-2層,爬到第n層有幾種爬法?
當遇到很複雜的題目時,想從小的測資開始慢慢帶,看有沒有規律存在:
有沒有感覺就是費氏數列?但為什麼是費氏數列?
題目說一次可以爬1層或2層,所以爬到第4層的時候一定是從第3層或第2層爬上來的,爬到第5層的時候一定是從第4層或第3層爬上來的,這就是為什麼是費氏數列!
class Solution(object):
def climbStairs(self, n):
"""
:type n: int
:rtype: int
"""
if (n <= 1):
return n
dp = [0] * (n + 1)
dp[1] = 1
dp[2] = 2
for i in range(3, n + 1):
dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2]
return dp[n]
